Jul 26, 202218: Organic Chemistry 18.12: Alcohols Expand/collapse global location 18.12: Alcohols Page ID Learning Objectives Identify the general structure for an alcohol. Identify the structural feature that classifies alcohols as primary, secondary, or tertiary. Name alcohols with both common names and IUPAC names
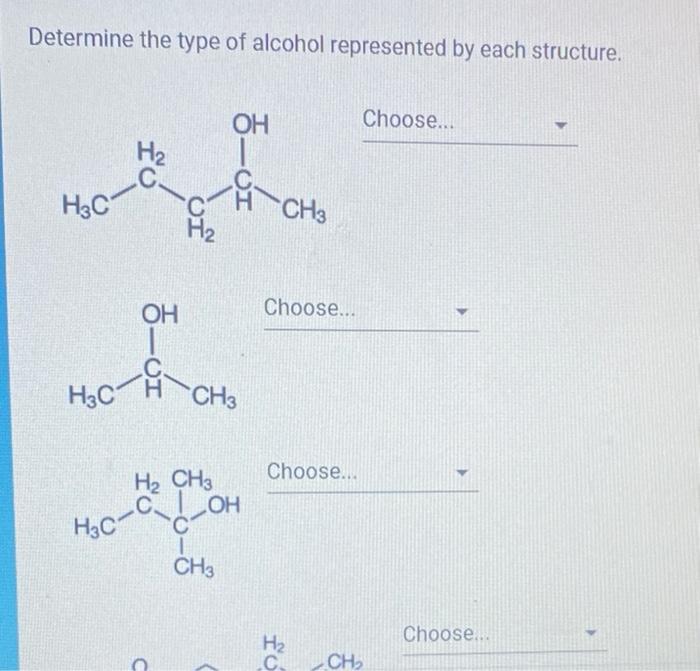
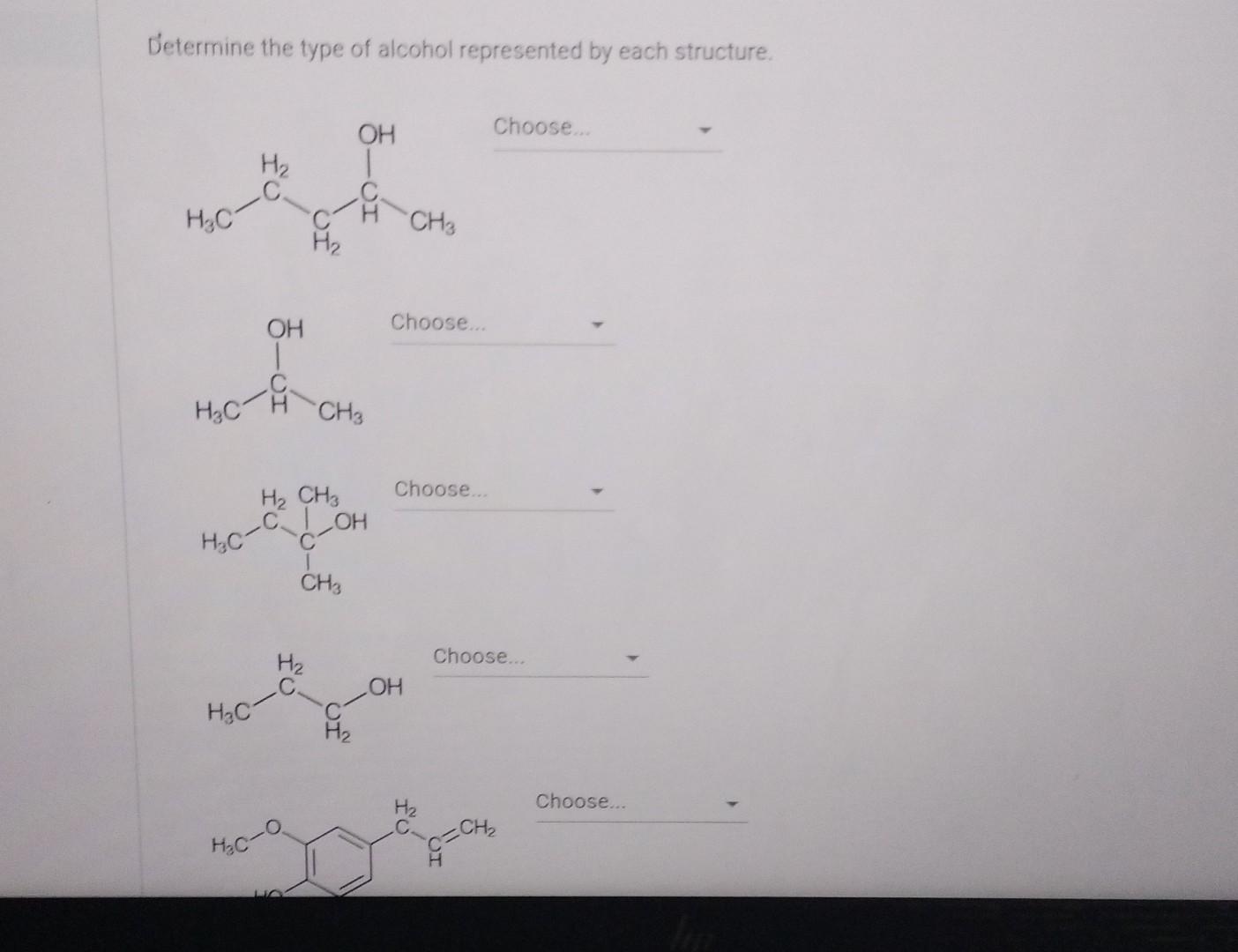
SOLVED: Determine the type of alcohol represented by each structure. HO Choose. Hz CH3 Choose. OH H3C CH3 Choose. CH2 H3C HO Choose; OH H3C CH3 Choose. OH
1. An alcohol with two other carbons attached to the carbon with the hydroxyl group = Secondary alcohol 2. An alcohol with one other carbon attached to the carbon with the hydroxyl group = Primary alcohol 3. 1-pentanol = Primary alcohol 4. 2-hexanol = Secondary alcohol 5. 3-ethyl-3-pentanol = Tertiary alcohol 6.

Source Image: reddit.com
Download Image
In a primary (1°) alcohol, the carbon atom that carries the -OH group is only attached to one alkyl group. Some examples of primary alcohols are shown below: Notice that the complexity of the attached alkyl group is irrelevant. In each case there is only one linkage to an alkyl group from the CH 2 group holding the -OH group. There is an
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Chemical Synthesis of the Cardiotonic Steroid Glycosides and Related Natural Products – Heasley – 2012 – Chemistry – A European Journal – Wiley Online Library Structure and classification of alcohols. Similar to water, an alcohol can be pictured as having an sp 3 hybridized tetrahedral oxygen atom with nonbonding pairs of electrons occupying two of the four sp 3 hybrid orbitals. (See chemical bonding for a discussion of hybrid orbitals.)Alkyl groups are generally bulkier than hydrogen atoms, however, so the R―O―H bond angle in alcohols is
![How to draw structures of alcohols |Full Structural Formula| Organic Chemistry [Online Video] – O Level Secondary Chemistry Tuition](https://icandochemistry942105908.files.wordpress.com/2022/02/picture1.png?w=1024)
Source Image: icandochemistry.com
Download Image
Determine The Type Of Alcohol Represented By Each Structure
Structure and classification of alcohols. Similar to water, an alcohol can be pictured as having an sp 3 hybridized tetrahedral oxygen atom with nonbonding pairs of electrons occupying two of the four sp 3 hybrid orbitals. (See chemical bonding for a discussion of hybrid orbitals.)Alkyl groups are generally bulkier than hydrogen atoms, however, so the R―O―H bond angle in alcohols is An alcohol is an organic compound with a hydroxyl (OH) functional group on an aliphatic carbon atom. Because OH is the functional group of all alcohols, we often represent alcohols by the general formula ROH, where R is an alkyl group.Alcohols are common in nature. Most people are familiar with ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the active ingredient in alcoholic beverages, but this compound is only one
How to draw structures of alcohols |Full Structural Formula| Organic Chemistry [Online Video] – O Level Secondary Chemistry Tuition
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Determine the type of alcohol corresponding to each given description or name. 1. 3-ethyl-3-pentanol 2. 1-pentanol 3. 2-hexanol 4. An alcohol with one other carbon attached to the carbon with the hydroxyl group 5. An alcohol with two other carbons attached to the carbon with the hydroxyl group 6. An alcohol with three other Chemical structure of the alcohol products (peak 6-10) products of… | Download Scientific Diagram

Source Image: researchgate.net
Download Image
Solved Determine the type of alcohol represented by each | Chegg.com Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Determine the type of alcohol corresponding to each given description or name. 1. 3-ethyl-3-pentanol 2. 1-pentanol 3. 2-hexanol 4. An alcohol with one other carbon attached to the carbon with the hydroxyl group 5. An alcohol with two other carbons attached to the carbon with the hydroxyl group 6. An alcohol with three other
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
SOLVED: Determine the type of alcohol represented by each structure. HO Choose. Hz CH3 Choose. OH H3C CH3 Choose. CH2 H3C HO Choose; OH H3C CH3 Choose. OH Jul 26, 202218: Organic Chemistry 18.12: Alcohols Expand/collapse global location 18.12: Alcohols Page ID Learning Objectives Identify the general structure for an alcohol. Identify the structural feature that classifies alcohols as primary, secondary, or tertiary. Name alcohols with both common names and IUPAC names

Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
Chemical Synthesis of the Cardiotonic Steroid Glycosides and Related Natural Products – Heasley – 2012 – Chemistry – A European Journal – Wiley Online Library In a primary (1°) alcohol, the carbon atom that carries the -OH group is only attached to one alkyl group. Some examples of primary alcohols are shown below: Notice that the complexity of the attached alkyl group is irrelevant. In each case there is only one linkage to an alkyl group from the CH 2 group holding the -OH group. There is an

Source Image: chemistry-europe.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Download Image
SOLVED: Determine the type of alcohol represented by each structure. HO Choose. Hz CH3 Choose. OH H3C CH3 Choose. CH2 H3C HO Choose; OH H3C CH3 Choose. OH An alcohol is an organic compound with a hydroxyl (OH) functional group on an aliphatic carbon atom.

Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
Sparkling Wine Cocktails 101 | Alcohol Professor Structure and classification of alcohols. Similar to water, an alcohol can be pictured as having an sp 3 hybridized tetrahedral oxygen atom with nonbonding pairs of electrons occupying two of the four sp 3 hybrid orbitals. (See chemical bonding for a discussion of hybrid orbitals.)Alkyl groups are generally bulkier than hydrogen atoms, however, so the R―O―H bond angle in alcohols is

Source Image: alcoholprofessor.com
Download Image
Ethanol Formula Structure, Molar Mass, Uses and Properties An alcohol is an organic compound with a hydroxyl (OH) functional group on an aliphatic carbon atom. Because OH is the functional group of all alcohols, we often represent alcohols by the general formula ROH, where R is an alkyl group.Alcohols are common in nature. Most people are familiar with ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the active ingredient in alcoholic beverages, but this compound is only one

Source Image: chemicalslearning.com
Download Image
Solved Determine the type of alcohol represented by each | Chegg.com
Ethanol Formula Structure, Molar Mass, Uses and Properties 1. An alcohol with two other carbons attached to the carbon with the hydroxyl group = Secondary alcohol 2. An alcohol with one other carbon attached to the carbon with the hydroxyl group = Primary alcohol 3. 1-pentanol = Primary alcohol 4. 2-hexanol = Secondary alcohol 5. 3-ethyl-3-pentanol = Tertiary alcohol 6.
Chemical Synthesis of the Cardiotonic Steroid Glycosides and Related Natural Products – Heasley – 2012 – Chemistry – A European Journal – Wiley Online Library Sparkling Wine Cocktails 101 | Alcohol Professor An alcohol is an organic compound with a hydroxyl (OH) functional group on an aliphatic carbon atom.